1,3-BUTANEDIOL (1,3-BDO)
A building block for many high value products including pheromones, fragrances, insecticides, antibiotics and synthetic rubber.
Factfile
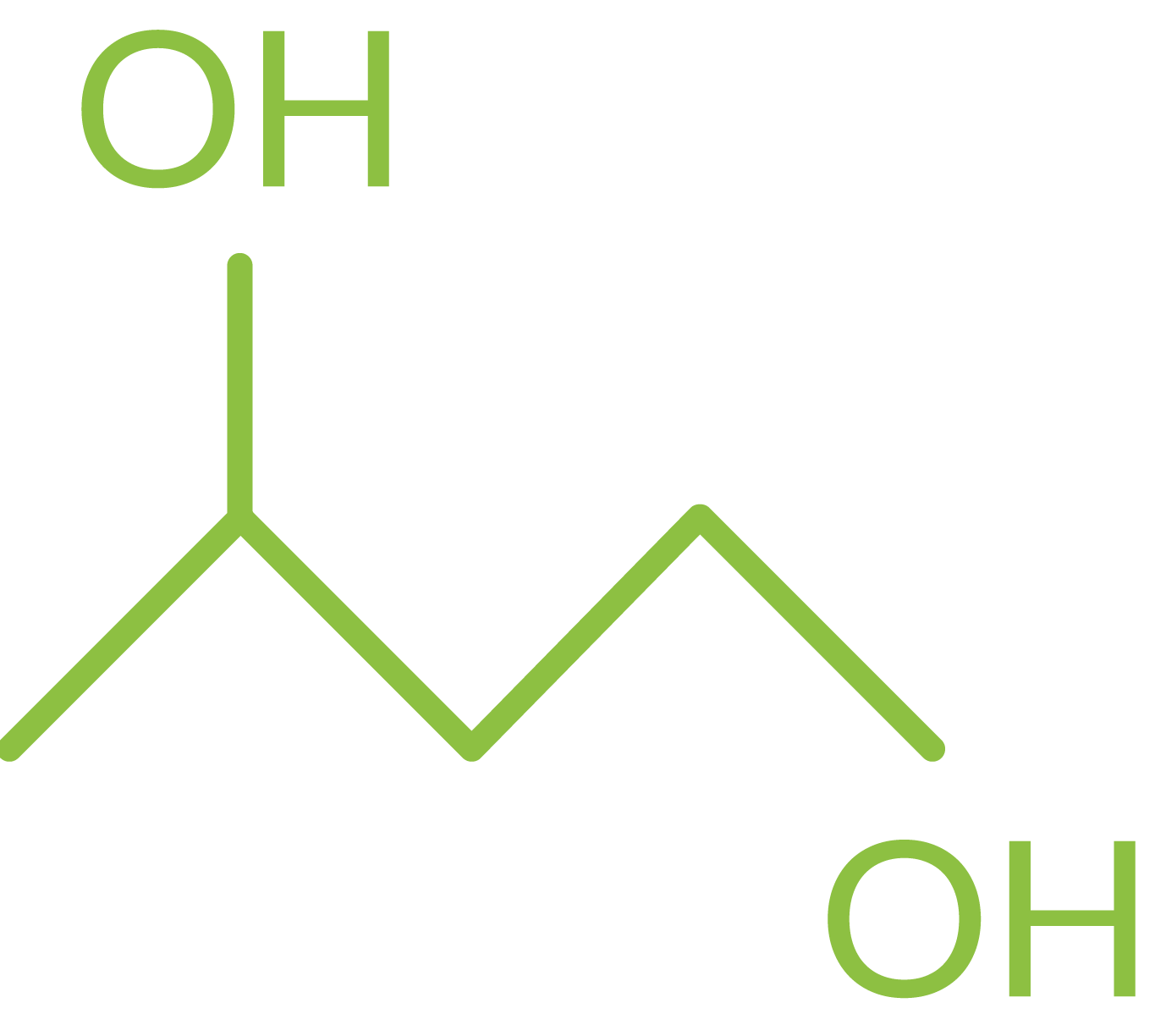
Name: 1,3-butanediol
Synonyms: 1,3-butandiol, 1,3 butylene glycol
CAS Number: 107-88-0, (R)6290-03-5, (S) 24621-61-2
Molecular formula: C4H10O2
MW: 90.12 g mol-1
Patents related to synthesis: 44
Why is it of interest?
1,3 butanediol (1,3-BDO) is a short chain compound containing both a primary and a secondary alcohol. It has a number of uses and applications, primarily as a humectant in the cosmetic industry and also in the flavour and fragrance industry. Like all diols it can be applied in the synthesis of polyesters where the branching gives rise to differing properties. It is also used as a platform molecule in the production of pharmaceutical relevant compounds, most notably beta lactam antibiotics. The market for 1,3-BDO is small but relatively well established, however the petrochemical route to its production is multi-stepped and relatively expensive. As such a simple bio-derived route is highly attractive.
Feedstocks
The current industrial route to 1,3-BDO is via 4 hydroxy-butanone, using either chemocatalytic reduction to give a racemic product followed by biocatalytic resolution to the optically pure isomer if desired, or by whole cell asymmetric reduction. Bio-derived chemocatalytic pathways require the use of the C4 sugar erythritol which is produced industrially as a sweetener but is very high cost. This route of production has poor selectivity, giving a variety of diols, mainly for use in the production of polyols or olefins. A more promising route is the use of synthetic biology to engineer a route to 1,3-BDO via fermentation. This is still very much in the early stages of investigation, with various pathways under analysis but is the most likely to yield an industrially viable process. Finally, a 4 step route starting from the amino acid theronine is also known, but not applicable at scale.
Applications

The highest cost current application of BDO is as a precursor to beta-lactams which constitute the most commonly used antibiotics. Although many antibiotics can generally be manufactured bio-catalytically, roughly 75% of penicillin produced is consumed as feedstock in the formation of semi synthetic antibiotics. Many of these class of antibiotics require optically pure (R)-1,3-BDO in their synthesis, specifically penems and carbapenems. The other major use is in the cosmetics industry where a high grade of BDO is required in order to eliminate odorous side products from the industrial route. High purity 1,3-BDO is utilised as a low volatility moisturising agent, as well as helping to disperse hydrophobic and hydrophilic components in cosmetic formulations and imparting antibacterial properties.
THE TOP TEN
